A Comprehensive Guide to Retirement Savings: Understanding 401(k) Contributions in 2017
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Retirement Savings: Understanding 401(k) Contributions in 2017
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Retirement Savings: Understanding 401(k) Contributions in 2017. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Retirement Savings: Understanding 401(k) Contributions in 2017

Retirement planning is a crucial aspect of financial well-being. One of the most powerful tools available to individuals is the 401(k) plan, a retirement savings plan offered by many employers. Understanding how 401(k) contributions work, particularly in the context of 2017, can significantly impact long-term financial security. This article provides a comprehensive guide to 401(k) contributions for 2017, delving into its mechanics, benefits, and relevant considerations.
What are 401(k) Contributions?
A 401(k) plan allows employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income to a retirement savings account. These contributions are deducted from an employee’s paycheck and invested in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. The funds grow tax-deferred, meaning that taxes are not paid until retirement. This tax advantage significantly enhances the potential for long-term wealth accumulation.
Key Features of 401(k) Contributions in 2017:
- Contribution Limits: In 2017, the annual contribution limit for 401(k) plans was $18,000. Individuals aged 50 and over could contribute an additional $6,000, bringing the total to $24,000. These limits have been adjusted in subsequent years, but understanding the 2017 figures provides a historical context.
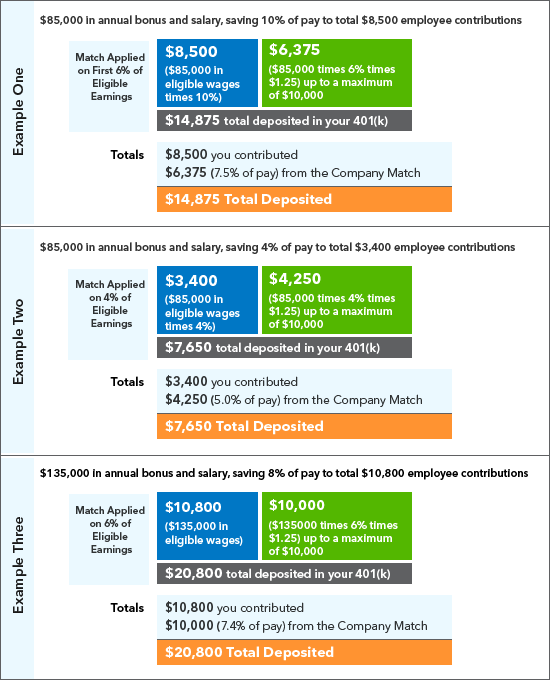
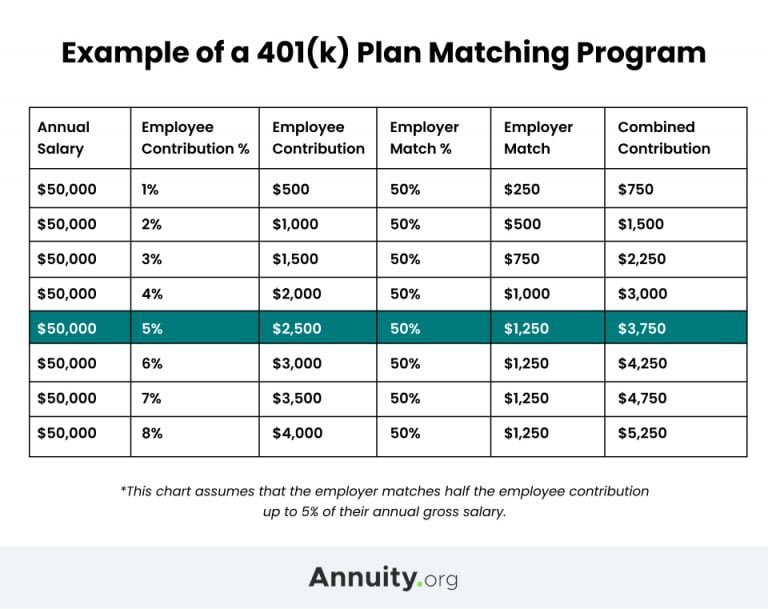
- Employer Matching: Many employers offer matching contributions to their employees’ 401(k) accounts. This means that for every dollar an employee contributes, the employer contributes a certain percentage, often up to a specified limit. This employer match is essentially free money and significantly boosts retirement savings.
- Investment Options: 401(k) plans typically offer a range of investment options, allowing individuals to tailor their portfolio based on their risk tolerance and investment goals. These options can include mutual funds, index funds, target-date funds, and other investment vehicles.
- Tax Advantages: The tax-deferred growth of 401(k) contributions is a significant advantage. Individuals do not pay taxes on the earnings until they withdraw the funds in retirement. This allows the invested funds to grow more rapidly, leading to a larger retirement nest egg.
Benefits of 401(k) Contributions:
- Tax Savings: 401(k) contributions are made with pre-tax income, resulting in immediate tax savings. This can significantly reduce an individual’s tax liability in the current year.
- Compounding Growth: The power of compounding is a key advantage of 401(k) contributions. As the invested funds grow, they earn interest or dividends, which then earn further interest or dividends. This exponential growth creates a substantial return over time.
- Financial Security in Retirement: 401(k) contributions provide a vital source of income for retirement. By saving consistently over the working years, individuals can build a substantial retirement nest egg that can support their lifestyle after they stop working.
- Employer Matching: The employer match is a free gift that significantly boosts retirement savings. This additional contribution from the employer effectively increases the rate of return on an individual’s contributions.
Considerations for 401(k) Contributions in 2017:
- Investment Strategy: It is essential to develop a sound investment strategy for 401(k) contributions. This strategy should be tailored to an individual’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon.
- Diversification: Diversifying investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, can help mitigate risk and maximize returns.
- Fees: 401(k) plans may have associated fees, including administrative fees and investment management fees. It is crucial to understand these fees and compare them across different plans.
- Withdrawal Rules: There are specific rules governing withdrawals from 401(k) accounts. Early withdrawals before age 59 1/2 are generally subject to a 10% penalty and income taxes.
FAQs on 401(k) Contributions in 2017:
1. What happens to my 401(k) contributions when I change jobs?
When you change jobs, you have several options for your 401(k) account:
- Rollover: You can roll over your 401(k) balance into a new employer’s plan or into an Individual Retirement Account (IRA).
- Cash Out: You can withdraw the funds, but you will be subject to taxes and potentially a 10% penalty if you are under age 59 1/2.
- Leave it in the account: You can leave your funds in the previous employer’s plan, but you may have limited investment options and access.
2. Can I contribute more than the annual limit?
No, you cannot contribute more than the annual limit for 401(k) contributions. Exceeding the limit will result in penalties.
3. Can I contribute to both a 401(k) and an IRA?
Yes, you can contribute to both a 401(k) and an IRA, but there are contribution limits for each. In 2017, the maximum contribution to a traditional IRA was $5,500 for individuals under 50 and $6,500 for those 50 and older.
4. What if I don’t have a 401(k) plan through my employer?
If your employer does not offer a 401(k) plan, you can open an IRA. An IRA is a personal retirement savings account that allows individuals to contribute pre-tax income, similar to a 401(k).
5. How do I choose the right investment options for my 401(k)?
Choosing investment options for your 401(k) depends on your risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. Consider factors such as:
- Risk Tolerance: How much risk are you comfortable taking with your investments?
- Investment Goals: What are your financial goals for retirement?
- Time Horizon: How long do you have until retirement?
Tips for Maximizing 401(k) Contributions in 2017:
- Start Early: The earlier you start contributing to a 401(k), the more time your investments have to grow.
- Contribute the Maximum: Take advantage of the full annual contribution limit to maximize your retirement savings.
- Take Advantage of Employer Matching: If your employer offers matching contributions, make sure you are contributing enough to receive the full match.
- Review Your Investment Strategy: Regularly review your investment strategy and make adjustments as needed to ensure it aligns with your goals and risk tolerance.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider consulting a financial advisor for personalized guidance on retirement planning and 401(k) contributions.
Conclusion:
401(k) contributions are an essential component of retirement planning. By understanding the mechanics, benefits, and considerations involved, individuals can make informed decisions that support their long-term financial security. The tax advantages, potential for compounding growth, and employer matching make 401(k) contributions a powerful tool for building a comfortable retirement. By taking advantage of this valuable resource, individuals can set themselves up for a financially secure future. It is important to note that the information provided in this article is for general knowledge and does not constitute financial advice. Consult with a qualified financial advisor for personalized guidance.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Retirement Savings: Understanding 401(k) Contributions in 2017. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!