The Art and Science of Decision-Making: Understanding the Process of Reaching a Conclusion
Related Articles: The Art and Science of Decision-Making: Understanding the Process of Reaching a Conclusion
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Art and Science of Decision-Making: Understanding the Process of Reaching a Conclusion. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art and Science of Decision-Making: Understanding the Process of Reaching a Conclusion

Decision-making is an integral aspect of human existence, permeating every facet of our lives. From trivial choices like what to eat for breakfast to significant life decisions such as career paths or relationship commitments, the ability to make informed and decisive choices is paramount. This process, often referred to as "making up one’s mind," involves a complex interplay of cognitive processes, emotional factors, and environmental influences.
The Cognitive Framework of Decision-Making
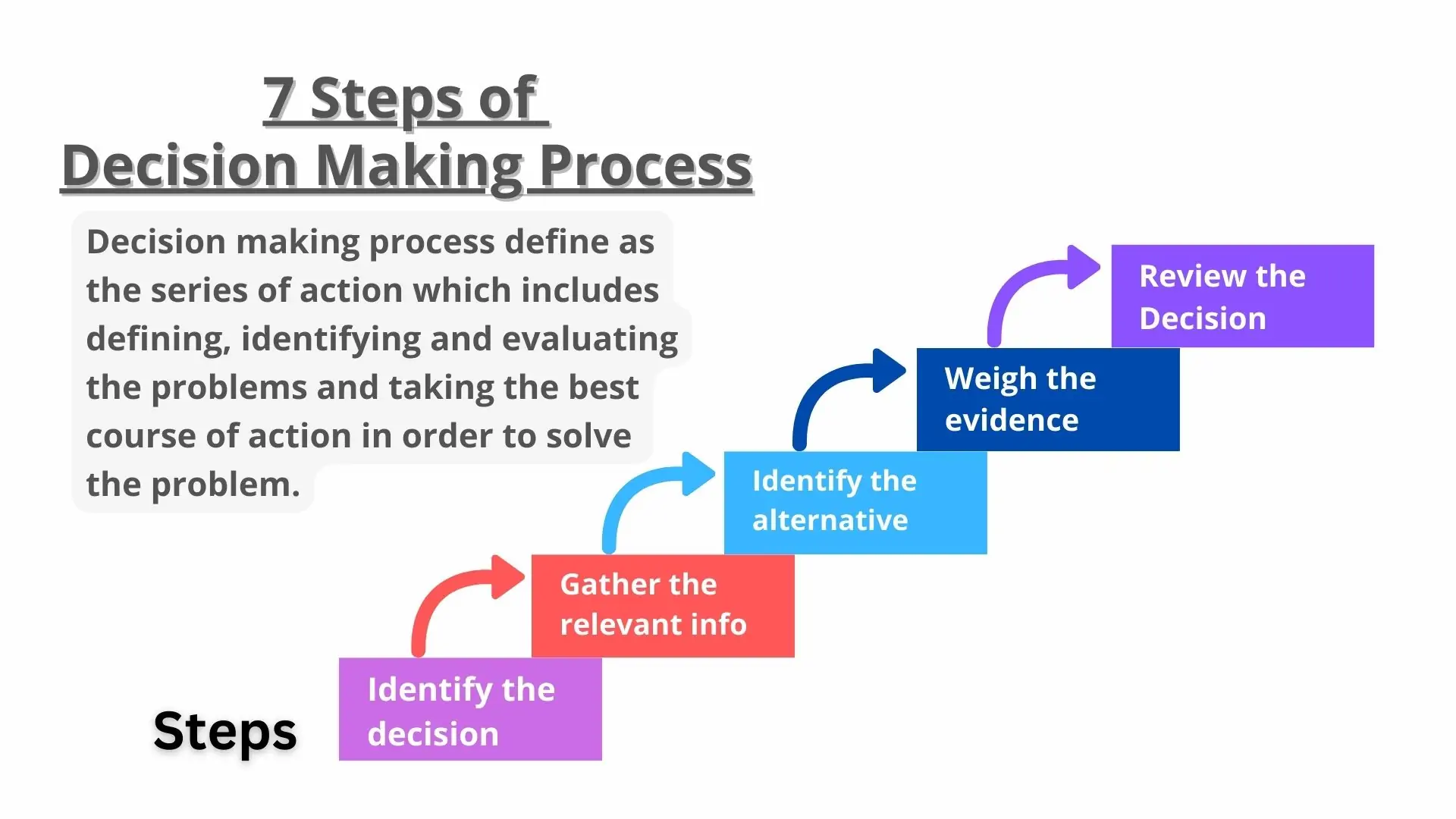
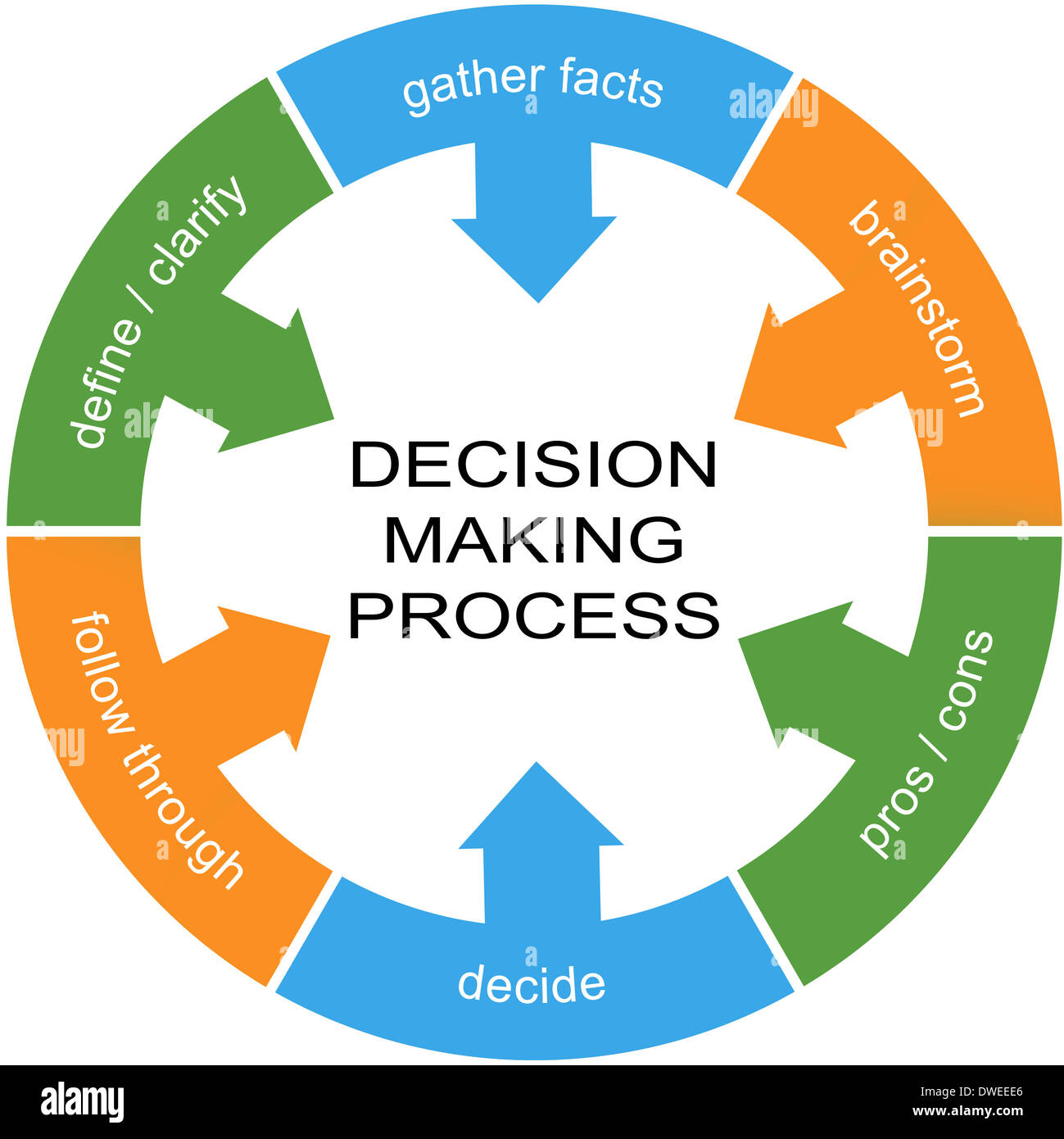
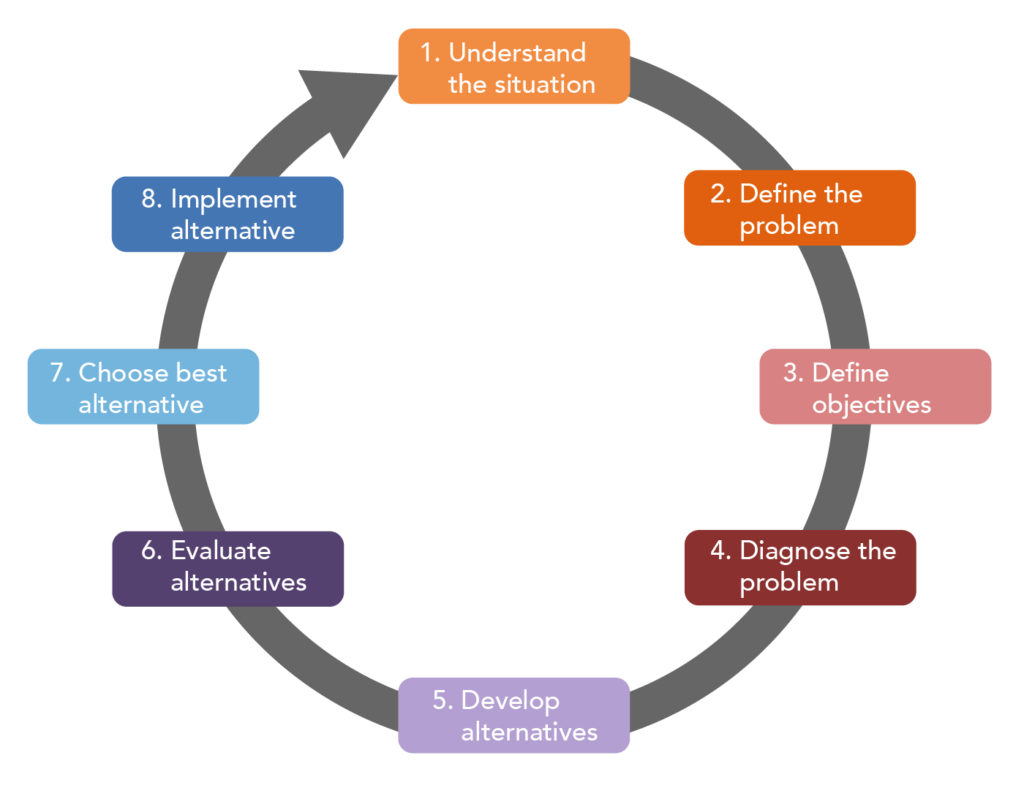
At its core, decision-making is a cognitive process that involves evaluating available options and selecting the most suitable course of action. This process can be broken down into distinct stages:
- Problem Recognition: The initial step involves identifying a need or a gap between the current state and a desired state. This recognition triggers the decision-making process.
- Information Gathering: Once a problem is identified, individuals gather information relevant to the decision. This involves seeking out data, opinions, and experiences to understand the potential options and their associated consequences.
- Option Generation: Based on the gathered information, individuals generate a range of potential solutions or courses of action. This step requires creativity and critical thinking to explore diverse possibilities.
- Evaluation of Options: Each option is then evaluated against specific criteria, such as feasibility, cost, risk, and potential benefits. This step involves weighing the pros and cons of each option and considering their potential impact.
- Selection and Implementation: After careful evaluation, individuals select the option deemed most appropriate. This decision is then implemented, and its effectiveness is monitored.
The Influence of Emotions and Biases
While decision-making is often portrayed as a purely rational process, emotions play a significant role in shaping our choices. Our feelings, beliefs, and values can influence our perception of information, leading to biases that impact our decision-making.
- Confirmation Bias: This bias refers to our tendency to seek out information that confirms our existing beliefs and ignore or dismiss evidence that contradicts them.
- Anchoring Bias: This bias occurs when we place undue weight on the first piece of information we receive, even if it is not necessarily accurate or relevant.
- Availability Bias: This bias arises from our tendency to overestimate the likelihood of events that are easily recalled or vivid in our minds.
- Framing Effects: The way information is presented can significantly influence our choices. For example, presenting the same option as a gain versus a loss can lead to different decisions.
Factors Affecting Decision-Making
Numerous factors can influence the decision-making process, including:
- Individual Differences: Personality traits, cognitive abilities, and past experiences can all influence our decision-making styles.
- Social Influences: The opinions and expectations of others, particularly those in our social networks, can significantly affect our choices.
- Contextual Factors: The environment in which a decision is made, including time constraints, available resources, and cultural norms, can also play a role.
The Importance of Effective Decision-Making
Making sound decisions is crucial for personal and professional success. Here are some key benefits:
- Improved Outcomes: Effective decision-making leads to better outcomes in various aspects of life, from career advancement to personal well-being.
- Increased Confidence: Making informed choices can boost confidence and self-efficacy, leading to a more positive outlook and a greater sense of control.
- Reduced Stress: By making decisions proactively, individuals can reduce stress and anxiety associated with uncertainty and indecision.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: The decision-making process itself strengthens problem-solving skills and fosters a more analytical mindset.
Strategies for Improving Decision-Making
While decision-making is a complex process, there are several strategies individuals can employ to enhance their ability to make informed and effective choices:
- Gather Comprehensive Information: Seek out diverse perspectives and data sources to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the situation and potential options.
- Consider All Options: Explore a wide range of possibilities, even those that seem unconventional or challenging, to avoid limiting your choices.
- Evaluate Options Objectively: Use a structured approach to evaluate options, considering both pros and cons, and strive to minimize the influence of emotions and biases.
- Seek Feedback: Consult with trusted individuals or experts to gain insights and perspectives that can help you make a more informed decision.
- Practice Mindfulness: Cultivate mindfulness and emotional awareness to better understand your own biases and emotional responses to different options.
- Develop a Decision-Making Framework: Create a structured process for decision-making that you can consistently apply to different situations.
- Embrace Flexibility: Be prepared to adjust your decision based on new information or changing circumstances.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Decision-Making
Q: What are some common decision-making traps to avoid?
A: Common decision-making traps include:
- Overconfidence Bias: Overestimating your knowledge and abilities can lead to poor decisions.
- Sunk Cost Fallacy: Continuing to invest in a failing course of action simply because you’ve already invested significant resources.
- Groupthink: Conformity within a group can lead to poor decision-making if dissenting opinions are suppressed.
- Escalation of Commitment: Increasing your commitment to a failing course of action despite negative feedback.
Q: How can I overcome decision paralysis?
A: Decision paralysis occurs when individuals are overwhelmed by choices and unable to make a decision. To overcome this, try:
- Break down the decision: Divide the decision into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Set a deadline: Having a deadline can help you focus and overcome procrastination.
- Use a decision matrix: This tool can help you weigh different options against specific criteria.
- Seek professional guidance: If you’re struggling with a significant decision, consider consulting a therapist or coach.
Q: What are some tips for making difficult decisions?
A: Making difficult decisions requires careful consideration and emotional resilience. Here are some tips:
- Seek clarity: Define the problem clearly and identify your goals.
- Consider long-term consequences: Don’t focus solely on immediate gratification.
- Accept uncertainty: It’s impossible to predict the future with certainty.
- Trust your intuition: Your gut feeling can often provide valuable insights.
- Seek support: Talk to trusted friends, family, or professionals for guidance and support.
Conclusion
Decision-making is an essential life skill that requires a blend of cognitive, emotional, and social factors. By understanding the process and developing strategies to improve our decision-making skills, we can make more informed and effective choices that lead to positive outcomes in all areas of our lives. It is a continuous process of learning and refinement, and by embracing the challenges and opportunities it presents, we can navigate the complexities of life with greater clarity, confidence, and success.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art and Science of Decision-Making: Understanding the Process of Reaching a Conclusion. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!