The Significance of a 30% Makeup: Navigating the World of Financial Reporting
Related Articles: The Significance of a 30% Makeup: Navigating the World of Financial Reporting
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Significance of a 30% Makeup: Navigating the World of Financial Reporting. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Significance of a 30% Makeup: Navigating the World of Financial Reporting
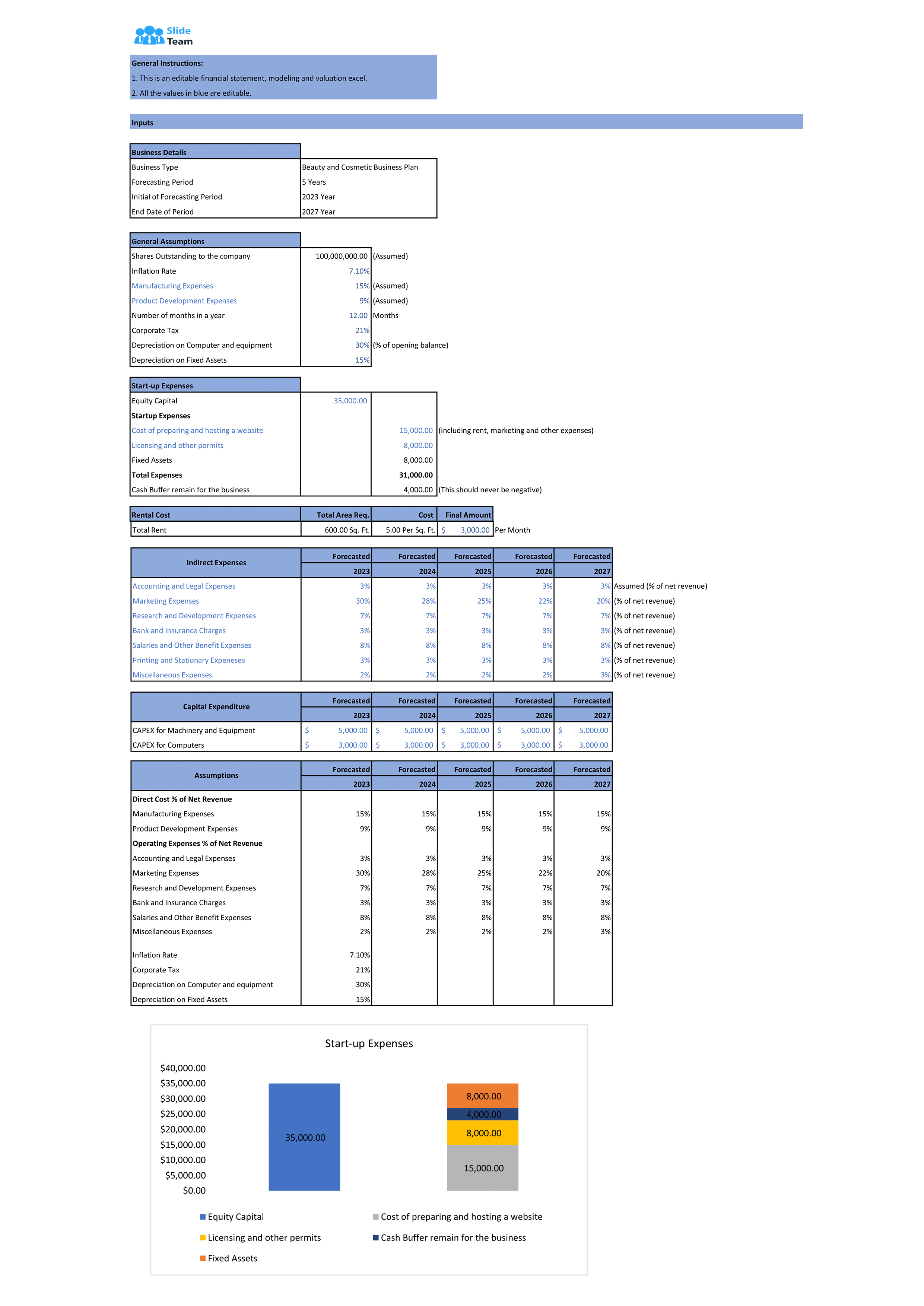
In the realm of financial reporting, the concept of "makeup" often arises, specifically in the context of a "30% makeup." This term, while seemingly straightforward, carries significant implications for understanding financial statements and their underlying complexities. This article aims to demystify the concept of a 30% makeup, providing a comprehensive understanding of its meaning, importance, and applications.
Defining the Concept: What is a 30% Makeup?
A 30% makeup, also known as a "30% threshold," refers to a specific financial reporting requirement that necessitates a company to disclose certain financial information when a particular event or transaction reaches a specific percentage threshold, typically 30%. This threshold is often applied to various aspects of financial reporting, including:
-
Significant Subsidiaries: If a company owns more than 30% of another company’s voting shares, it is generally considered a significant subsidiary. This triggers the requirement to consolidate the subsidiary’s financial statements with the parent company’s, providing a more comprehensive picture of the consolidated entity’s financial performance.
-
Equity Method Investments: When a company holds between 20% and 50% of another company’s voting shares, it typically uses the equity method to account for the investment. However, if the investment surpasses 30%, specific disclosure requirements may apply, including detailed information about the investment, its fair value, and any significant changes.
-
Related Party Transactions: Transactions between companies with a close relationship, such as parent and subsidiary, can be considered related party transactions. If the value of such transactions exceeds 30% of a company’s revenue or net income, detailed disclosures are usually required, highlighting the nature of the relationship, the terms of the transaction, and any potential impact on financial performance.
-
Contingent Liabilities: These are potential obligations that may arise depending on the occurrence of a future event. If the estimated value of a contingent liability exceeds 30% of a company’s net income, it is often required to be disclosed, along with the nature of the contingency and its potential impact on the company’s financial position.
Why is a 30% Makeup Important?
The 30% makeup serves as a crucial tool for ensuring transparency and accountability in financial reporting. Its significance lies in the following aspects:
-
Enhanced Transparency: By mandating disclosures when certain thresholds are met, the 30% makeup promotes transparency in financial reporting. Investors, creditors, and other stakeholders can gain a better understanding of the company’s financial position, performance, and risks.
-
Improved Decision-Making: The information disclosed due to the 30% makeup provides valuable insights for investors and creditors, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding investments, lending, and other financial transactions.
-
Reduced Information Asymmetry: The 30% makeup helps to reduce information asymmetry, where certain stakeholders have more information than others. This promotes a more level playing field for all parties involved in financial decision-making.
-
Early Warning Signals: The 30% makeup can act as an early warning signal for potential risks or issues that may impact a company’s financial performance. By disclosing information related to significant subsidiaries, related party transactions, or contingent liabilities, the 30% makeup can alert stakeholders to potential challenges.
Applications and Examples of a 30% Makeup
The 30% makeup finds applications in various financial reporting frameworks, including:
-
U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP): GAAP outlines specific disclosure requirements based on the 30% threshold for significant subsidiaries, equity method investments, and other financial reporting elements.
-
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS): IFRS also incorporates the 30% makeup in its disclosure requirements, ensuring consistency in financial reporting across different jurisdictions.
-
Industry-Specific Regulations: Certain industries may have specific regulations or guidelines that incorporate the 30% makeup, tailoring disclosure requirements to their unique circumstances.
Examples:
-
Significant Subsidiary: A company owns 35% of the voting shares of another company. This ownership surpasses the 30% threshold, requiring the company to consolidate the subsidiary’s financial statements into its own.
-
Equity Method Investment: A company holds 40% of the voting shares of another company. This investment falls within the 30% threshold for equity method investments, requiring detailed disclosures about the investment’s fair value and its impact on the company’s financial performance.
-
Related Party Transaction: A company sells goods to its subsidiary for $10 million, representing 35% of the parent company’s revenue. This exceeds the 30% threshold, requiring the company to disclose the nature of the transaction, the terms of the agreement, and any potential impact on the company’s financial performance.
FAQs Regarding a 30% Makeup
Q: What happens if a company’s ownership in another company falls below 30% after exceeding the threshold?
A: If a company’s ownership falls below 30%, it may no longer be required to consolidate the subsidiary’s financial statements or apply the equity method. However, specific disclosure requirements may still apply based on the nature of the investment and its impact on the company’s financial performance.
Q: Can the 30% threshold vary depending on the industry or company size?
A: While 30% is a common threshold, specific industry regulations or company-specific policies may establish different thresholds. It’s important to refer to relevant reporting standards and company policies for accurate information.
Q: What are the penalties for non-compliance with the 30% makeup requirements?
A: Failure to comply with the 30% makeup requirements can lead to various penalties, including fines, regulatory investigations, and reputational damage. It’s crucial for companies to ensure they meet all applicable disclosure requirements.
Tips for Navigating the 30% Makeup
-
Consult with Financial Professionals: Seek guidance from qualified accountants or financial advisors to ensure compliance with the 30% makeup requirements and understand the specific implications for your company.
-
Review Financial Reporting Standards: Familiarize yourself with the relevant financial reporting standards, such as GAAP or IFRS, to understand the specific disclosure requirements for the 30% makeup.
-
Establish Clear Policies: Implement clear internal policies and procedures to ensure consistent application of the 30% makeup across all relevant transactions.
-
Monitor Financial Transactions: Actively track financial transactions to identify potential situations where the 30% makeup may apply, ensuring timely and accurate disclosures.
-
Maintain Adequate Documentation: Keep detailed records of all transactions and disclosures related to the 30% makeup to support compliance and demonstrate due diligence.
Conclusion
The 30% makeup plays a crucial role in promoting transparency and accountability in financial reporting. By mandating disclosures when specific thresholds are met, it provides valuable information to investors, creditors, and other stakeholders, enabling informed decision-making and reducing information asymmetry. Understanding the 30% makeup is essential for companies to ensure compliance with relevant reporting standards and maintain a strong financial reporting framework. By following the tips outlined in this article, companies can effectively navigate the complexities of the 30% makeup and contribute to a more transparent and robust financial reporting landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Significance of a 30% Makeup: Navigating the World of Financial Reporting. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!